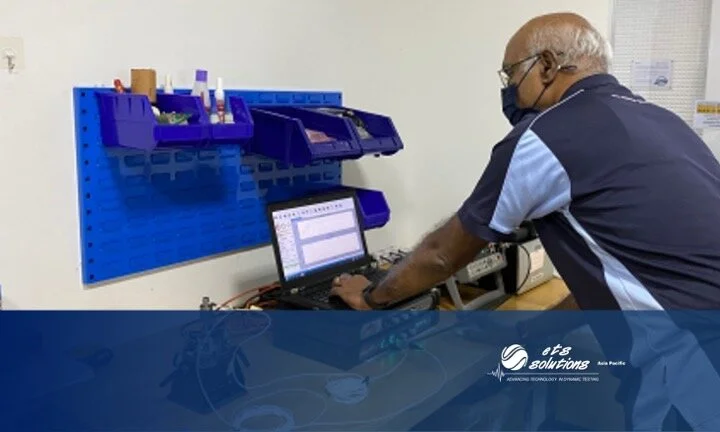
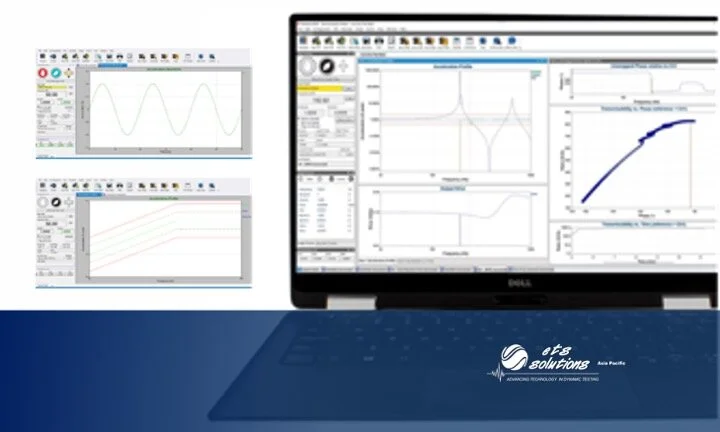
Vibration Testing is one such environmental test critical to the design process. All closed-loop vibration tests, consists of four main components: a vibration controller, an amplifier, a shaker, and a feedback sensor, together, these four components make up a vibration testing system. ETS Solutions Asia instruments vibration controllers control electrodynamic and hydraulic shakers from tabletop to warehouse size systems.
Different Types of Calibration
Measurement equipment calibration can be carried out on different types of instruments across different sectors. Electrical calibration refers to the process of verifying the performance of any instrument that measures or tests electrical parameters such as: voltage, current, resistance, inductance, capacitance, time and frequency. Mechanical instruments are subject to drift due to regular usage, mechanical shock and exposure to varying atmospheric conditions, as such mechanical calibration is needed.
The benefits of An Accredited Calibration Services Laboratory
The benefits of calibration include improving safety as well as saving money and increasing profitability by avoiding the costs of false acceptance and rejection of products, increasing production efficiency, and extending the life of the equipment. Since the standards of accredited calibration labs are set really high, you can be confident of the accuracy levels of the calibrations.
Sine Vibration Testing
Sine Vibration Testing may be considered as the most basic vibration testing method used. This type of vibration testing requires less complex parameters compare to other type of vibration testing. Knowing the nature of sinusoidal signal, makes this type of vibration testing easier to understand and to get familiar with. Though, easier to understand does not make it less important compare to other type of vibration testing. Sine vibration testing may still be at the top rank when we are thinking of dynamic characteristic measurement.
Factors That Affect The Accuracy of Measurements
Instrument calibration ensures that the instruments perform with high accuracy without compromising the final quality of the product. They perform best when they are calibrated following the manufacturers’ recommendations. Several factors may affect calibration, which will further affect the end quality, rendering the objective of calibration useless. Three of these factors are discussed in this article.